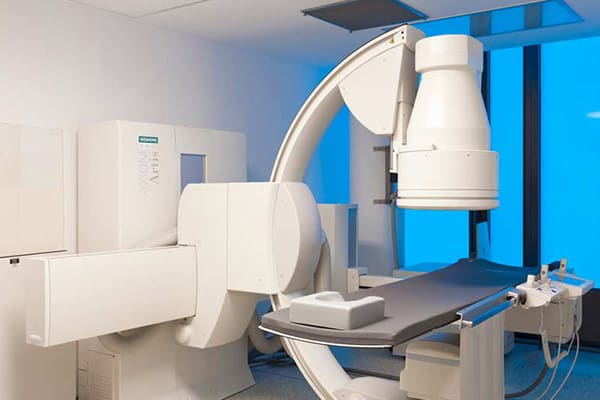
Angiography is a diagnostic procedure carried out by assistance of an MRI system, CT or a digital subtraction angiography device (DSA) for the depiction of vessels. MR angiography can take place with or without the application of a contrast agents, whereas CT or digital subtraction angiography necessitate the application of a contrast agent.
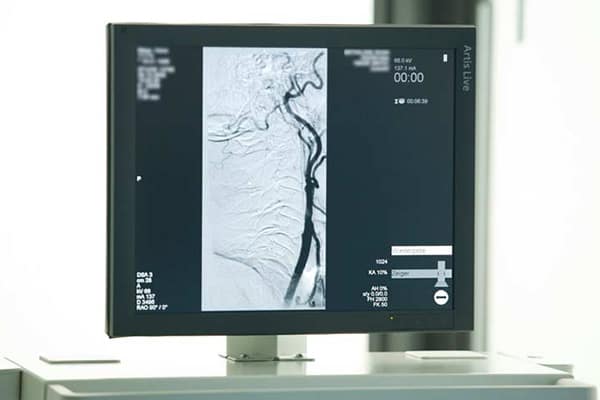
At the beginning of a digital subtraction angiography, an X-ray image without a contrast agent is taken. During and after the following contrast agent application, several further images are taken. The procedure is called digital subtraction angiography because the digitally taken images without a contrast agent are subtracted from the images depicting the vascular status with a contrast agent. This way elements of the images are removed that are not necessary for the evaluation or that would make it difficult to evaluate the images, for example, bones.