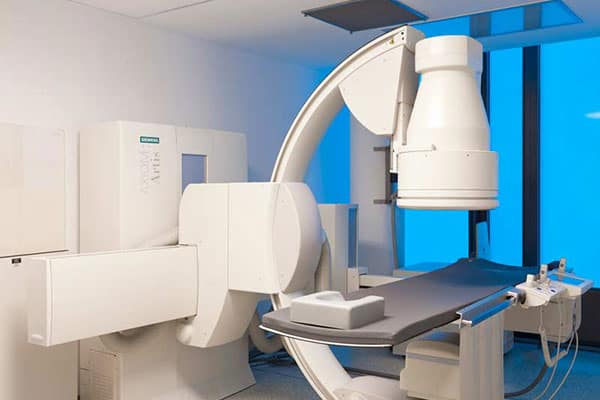
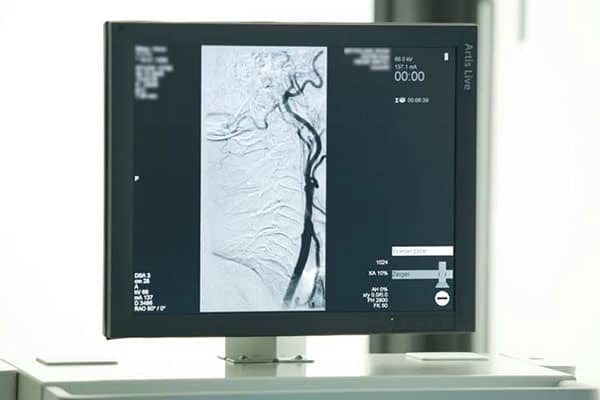
Angiography is a diagnostic procedure, carried out by assistance of an MRI system, CT or a digital subtraction angiography device (DSA) for the depiction of vessels. MR angiography can take place with or without the application of a contrast agents, whereas CT or digital subtraction angiography necessitate the application of a contrast agent.
Firstly, an X-ray image without a contrast agent is taken. During and after the following contrast agent application, several further images are taken. Because the digitized images without a contrast agent are subtracted from the images showing the vascular status with a contrast agent, the procedure is called digital subtraction angiography. This way elements of the images are removed that are not necessary for the evaluation or that would make it difficult to evaluate the images, for example, bones.