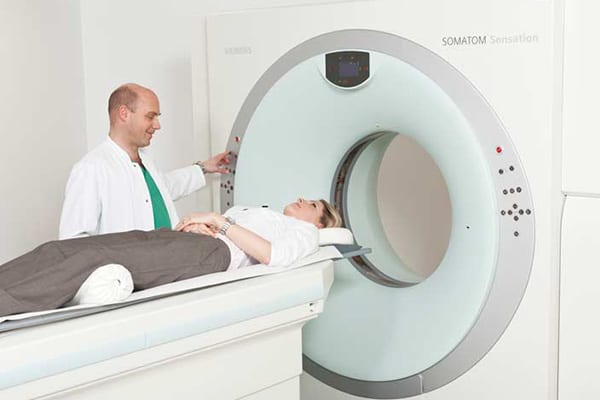
How is computed tomography carried out?
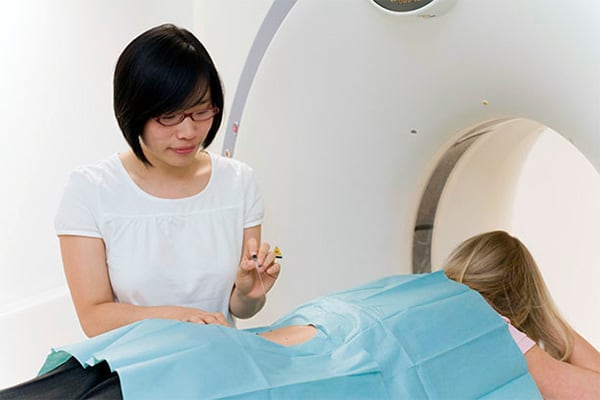
The core technology of computed tomography is X-ray technology. However, during CT examination X-ray pictures are taken from different directions. The X-ray tube and detectors rotate around the person and record up to 64 layers at the same time at high speed thanks to multislice spiral CT technology. High-performance computers compose anatomical images from these single layer data sets. The CT of Beta Klinik adapts the radiation dose automatically in real time during a CT examination. This makes the best radiation dose for every individual patient possible. Sometimes, it can be crucial to use a contrast agent in order to make specific characteristics of a certain tissue visible that would simply be invisible without it. Depending on the region to be examined, this contrast agent has to be administered orally, intravenously or intra-thecally (in the dural sac/spinal canal, e.g. in case of conventional myelography or CT myelography). If you have to take it orally, for example, you drink a certain amount of contrast agent before the examination. Since CT contrast agents contain iodine, the intravenous application can cause an (pseudo-)allergic reaction. Therefore, it is important to answer a few questions before the examination, also to figure out if you are allergic to iodine.
There are some contraindications for CT usage, i.e., reasons against undergoing a CT examination. These contraindications do not exclude CT usage in general. But an experienced physician has to decide if the CT examination can be carried out. The following contraindications are known:
- iodine allergy (relevant in case of intravenous application)
- reduced kidney function (kidney insufficiency
- hyperthyriodism
- careful use, only if indicated and applicable, in case of pregnancy and pediatric examinations